-
Figure 1. Sedimentation driven by centrifugal force
-
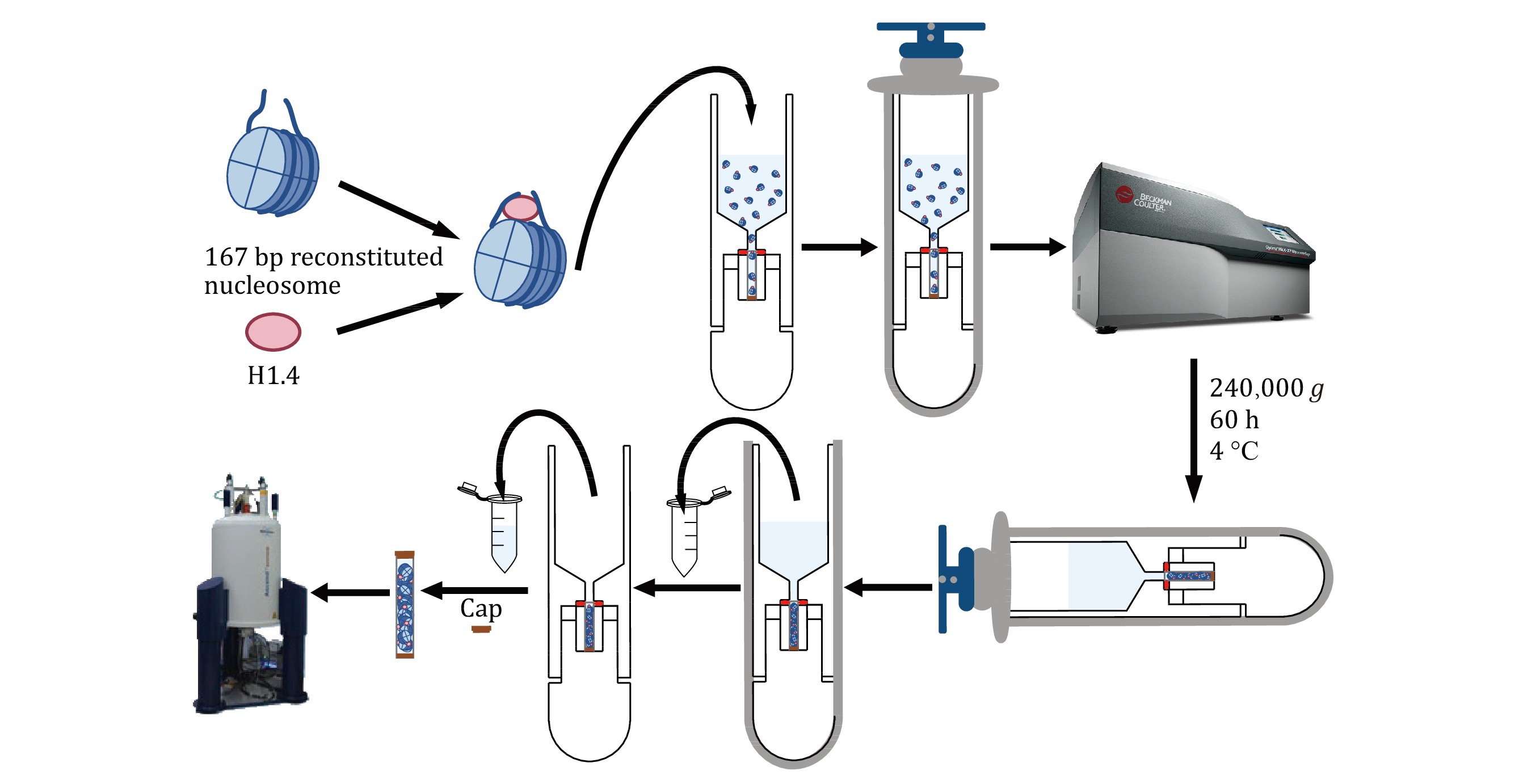
Figure 2. Technology roadmap of H1.4-NCP167 by sediment NMR
-
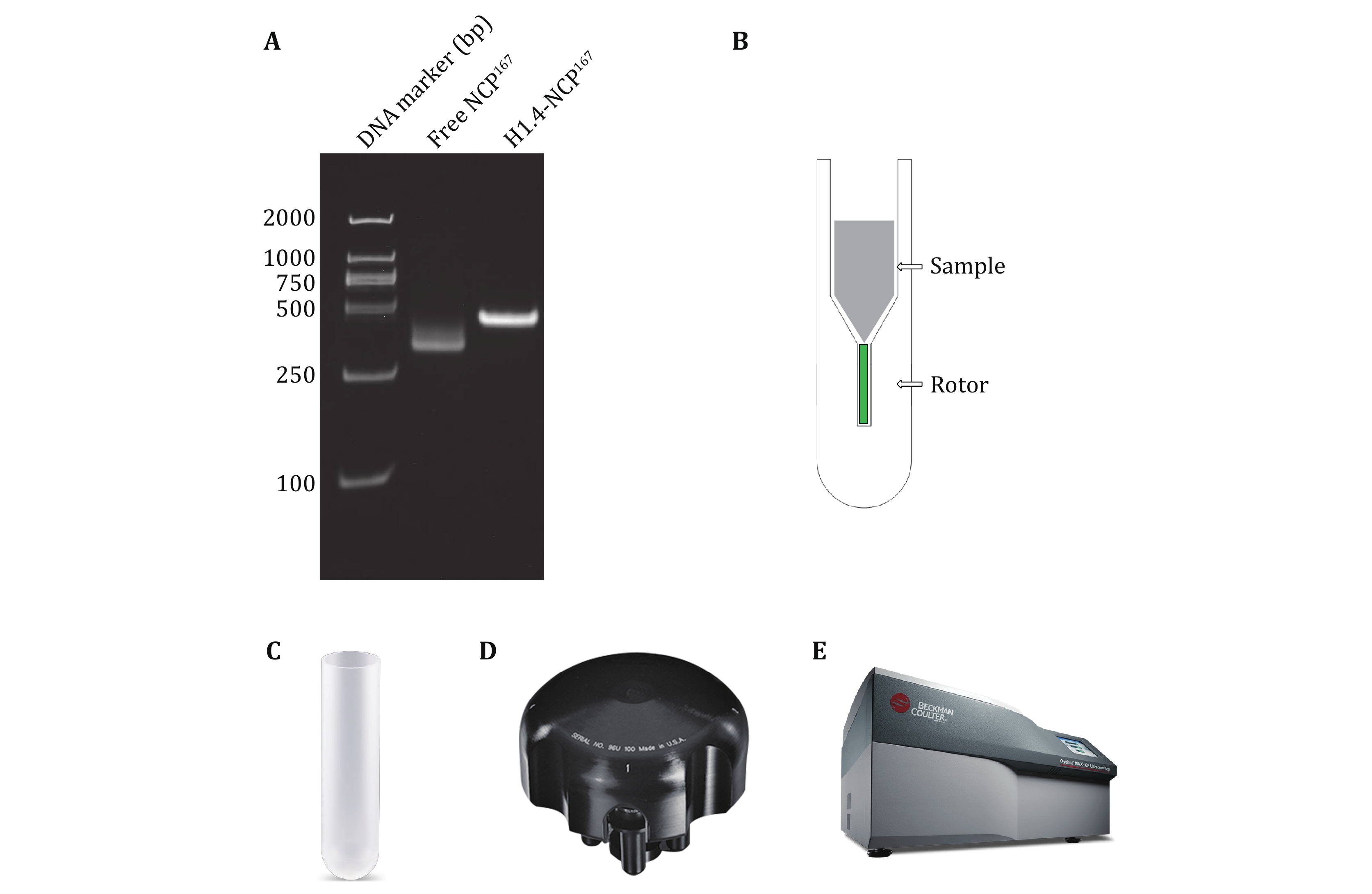
Figure 3. A Preparation of nucleosome complex H1.4-NCP167. Electrophoresis with 5% native PAGE, stained with GelRed. B Schematic diagram of optimized tool for sample loading. C An open-end-thin-walled polypropylene 5 mL centrifuge tube from Beckman Coulter.D Beckman Coulter MLS-50 Swinging-Bucket Rotor. E Beckman Coulter Optima MAX-XP Benchtop ultracentrifuge
-
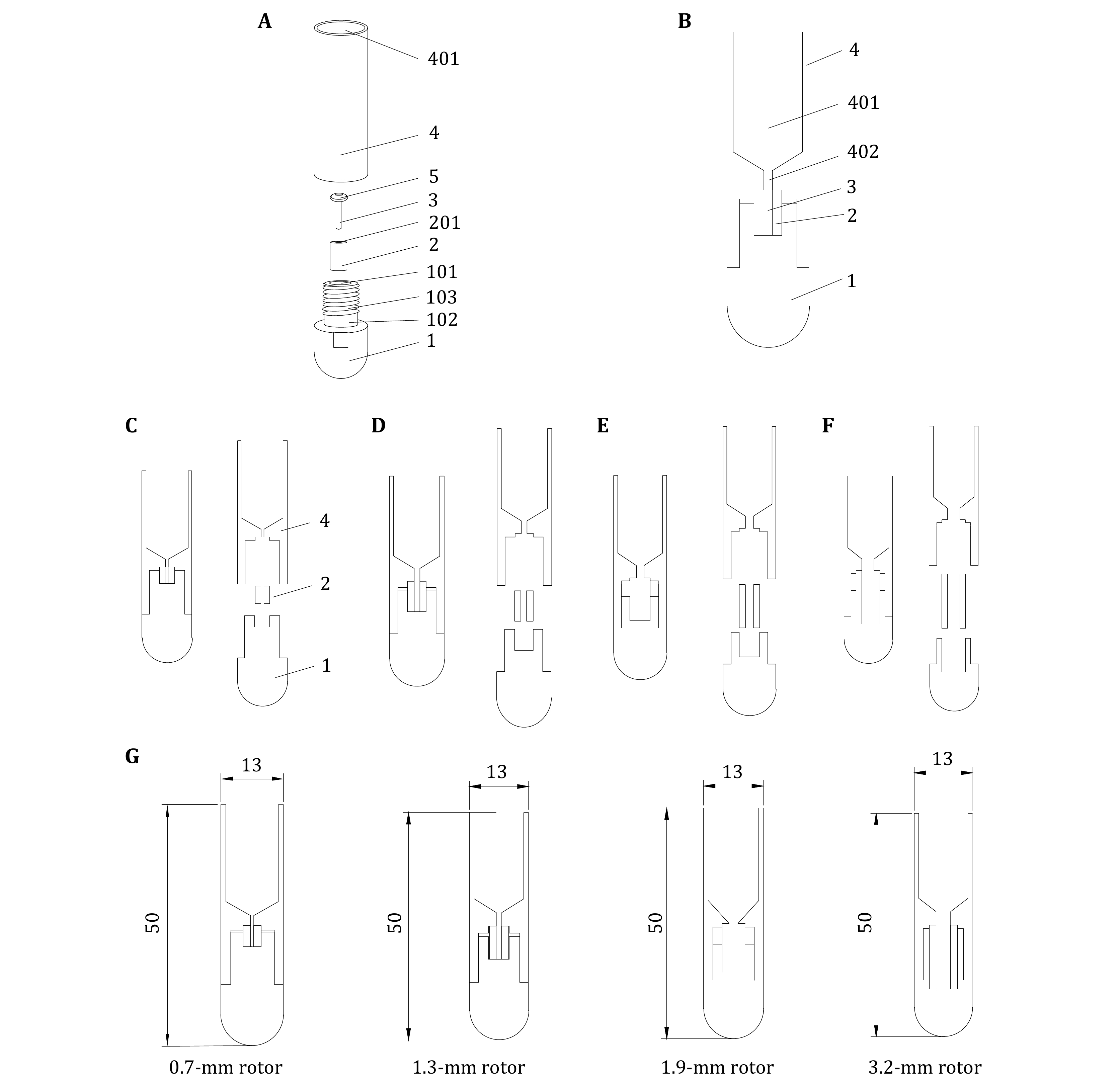
Figure 4. A Exploded view of 1.3-mm rotor sampling tool. B Cutaway drawing of 1.3-mm rotor sampling tool. C Plan of 0.7-mm sampling tool for ssNMR. D Plan of 1.3-mm sampling tool for ssNMR. E Plan of 1.9-mm sampling tool for ssNMR. F Plan of 3.2-mm sampling tool for ssNMR. G The size of the in-house tools
-
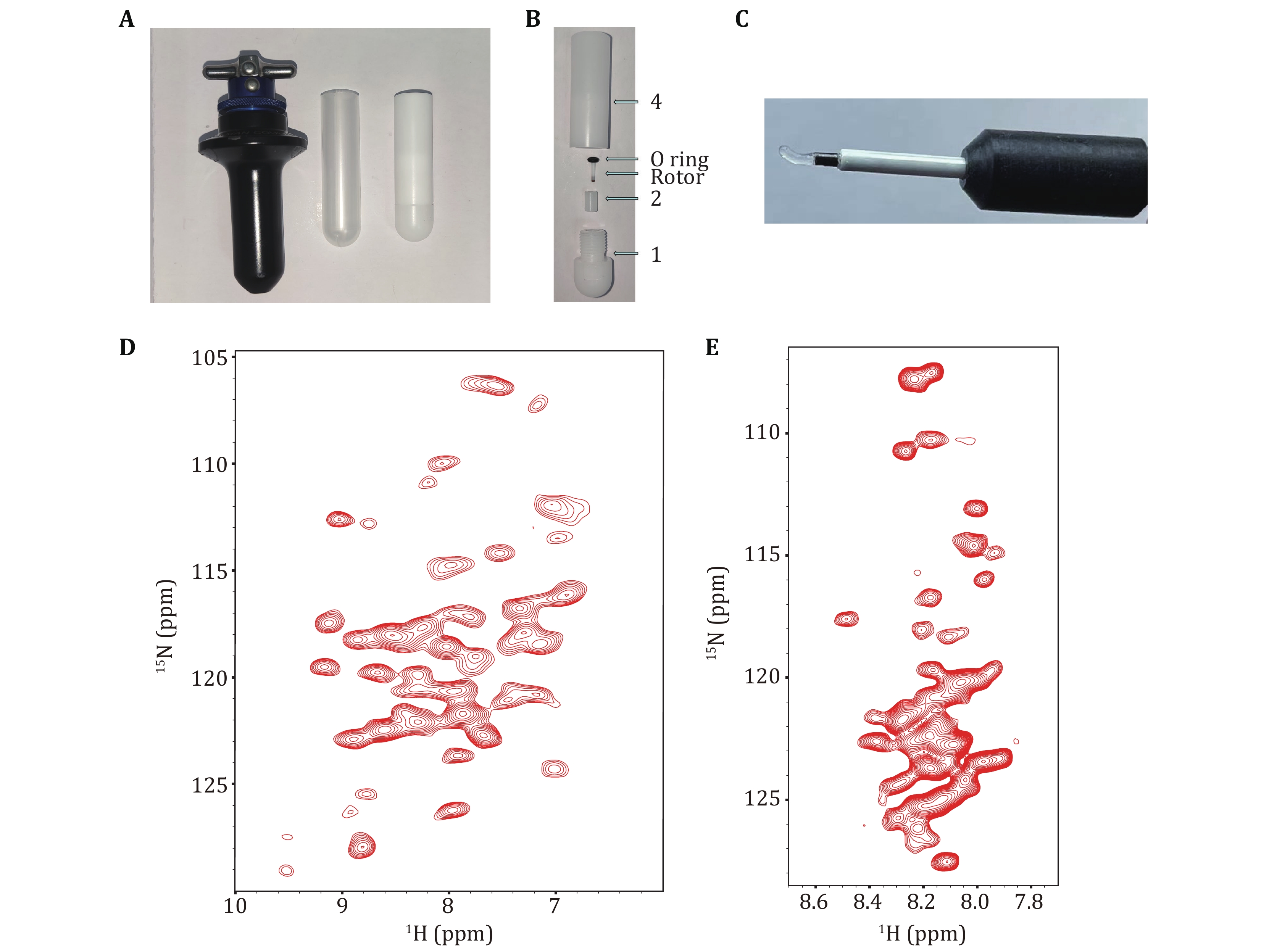
Figure 5. A Pictures displayed in Beckman Coulter MLS-50 Swinging-Bucket Rotor (left), a polypropylene centrifuge tube (13 × 51 mm) (middle), a sample loading tool of 1. 3-mm ssNMR rotor (right). B Physical display of the disassembly of the sampling tool with a 1.3-mm ssNMR rotor and O ring. C The transparent gel is the H1.4-NCP167 in a 1.3-mm ssNMR rotor obtained by ultracentrifugation sedimentation with a 1.3-mm ssNMR rotor loading tool. D CP-based 2D 1H-15N correlation spectrum of H1.4 (MAS = 55 kHz, Tset = 230K). E INEPT-based 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectrum of H1.4 (MAS = 60 kHz, Tset = 245K)
Figure
5 ,Table
5 个